Flu virus: Guidelines from Corfu Medical Association
flu
04 Feb 2019
/ 11:48
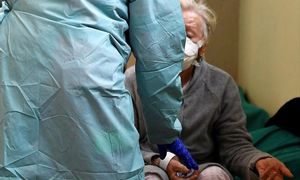
CORFU. With seasonal flu at its peak the number of cases with complications that require hospital care is increasing.
Epidemiologists at the Hellenic Centre for Disease Control & Prevention (KEELPNO) who are monitoring the situation say that the developments are as expected and advise people to stay calm.
The spread of the virus up to now is still within the expected limits and as yet there hasn't been any worrying mutation.
The fact that there hasn't been any mutation in the strain indicates that a large proportion of the vaccinations made available in October are providing protection against complications in the influenza virus.
Epidemiologists stress that in order to recover from flu without experiencing any complications it is especially important to seek medical help immediately so that treatment can also begin immediately if it is required.
Influenza symptoms usually appear suddenly and include high temperatures, pains in the muscles and joints, headaches, extreme tiredness, cattarh, sore throat and coughing (usually dry). Children may also have gastro-intestinal symptoms such as dizziness, vomiting and diarrhoea.
Symptoms appear 1 - 4 days after contracting the virus and last 2 - 7 days, although the coughing may continue considerably longer.
Adults can transmit the disease from 1 day before they become ill to 2 - 7 days after the symptons have appeared. Children can transmit it for over a week.
If children have the following symptoms, you should contact your doctor immediately:
- High, prolonged fever
- Tachypnoea (rapid breathing) or difficulty in breathing
- Cyanosis
- Refusal to take food or liquids
- Reduced activity, sleepiness
- Agitation or spasms
- Reappearance of fever or increase in coughing after improvement in flu symptoms
Adults need to have the following symptoms examined immediately:
- High, prolonged fever
- Difficulty in breathing
- Pain or a feeling of pressure in the chest
- Incidents of fainting
- Confusion
- A lot of or prolonged vomiting
The following are vulnerable groups:
- Those aged 60 and above
- Children under 6 months
- Those suffering from: asthma or other chronic pulmonary diseases, heart diseases, anaemia, diabetes, chronic kidney diseases, neuromuscular or neurological diseases.
- Immunosuppressed
- Those who have received transplants
- Those who are pregnant, new mothers or breastfeeding
- Those who are overweight
- Children who take aspirin long-term
- Those who look after young children
- Those who are institutionalised (live-in students, armed forces, residents of institutions)
- Health professionals
- Those involved in poultry farming
How can we protect ourselves and others?
Flu vaccination - it still isn't too late if someone hasn't already been vaccinated.
Meticulous observation of health precautions - Staying at home if we have the symptoms; covering our mouth when we cough or sneeze; immediately disposing of used paper tissues; avoiding contact with a lot of peopla and above all washing our hands thoroughly and regularly!
President - Dimitrios Kaloudis
General Secretary - Anastasia Apostolidou
The spread of the virus up to now is still within the expected limits and as yet there hasn't been any worrying mutation.
The fact that there hasn't been any mutation in the strain indicates that a large proportion of the vaccinations made available in October are providing protection against complications in the influenza virus.
Epidemiologists stress that in order to recover from flu without experiencing any complications it is especially important to seek medical help immediately so that treatment can also begin immediately if it is required.
Influenza symptoms usually appear suddenly and include high temperatures, pains in the muscles and joints, headaches, extreme tiredness, cattarh, sore throat and coughing (usually dry). Children may also have gastro-intestinal symptoms such as dizziness, vomiting and diarrhoea.
Symptoms appear 1 - 4 days after contracting the virus and last 2 - 7 days, although the coughing may continue considerably longer.
Adults can transmit the disease from 1 day before they become ill to 2 - 7 days after the symptons have appeared. Children can transmit it for over a week.
If children have the following symptoms, you should contact your doctor immediately:
- High, prolonged fever
- Tachypnoea (rapid breathing) or difficulty in breathing
- Cyanosis
- Refusal to take food or liquids
- Reduced activity, sleepiness
- Agitation or spasms
- Reappearance of fever or increase in coughing after improvement in flu symptoms
Adults need to have the following symptoms examined immediately:
- High, prolonged fever
- Difficulty in breathing
- Pain or a feeling of pressure in the chest
- Incidents of fainting
- Confusion
- A lot of or prolonged vomiting
The following are vulnerable groups:
- Those aged 60 and above
- Children under 6 months
- Those suffering from: asthma or other chronic pulmonary diseases, heart diseases, anaemia, diabetes, chronic kidney diseases, neuromuscular or neurological diseases.
- Immunosuppressed
- Those who have received transplants
- Those who are pregnant, new mothers or breastfeeding
- Those who are overweight
- Children who take aspirin long-term
- Those who look after young children
- Those who are institutionalised (live-in students, armed forces, residents of institutions)
- Health professionals
- Those involved in poultry farming
How can we protect ourselves and others?
Flu vaccination - it still isn't too late if someone hasn't already been vaccinated.
Meticulous observation of health precautions - Staying at home if we have the symptoms; covering our mouth when we cough or sneeze; immediately disposing of used paper tissues; avoiding contact with a lot of peopla and above all washing our hands thoroughly and regularly!
President - Dimitrios Kaloudis
General Secretary - Anastasia Apostolidou